How Google Sees Client-Side Rendered Pages on Lovable
Summarize with AI
Get instant summaries and insights from this article using AI tools
You built an amazing app on Lovable. It loads instantly, feels interactive, and even has built-in AI features.
But when you search for it on Google, nothing shows up.
Welcome to one of the most common pain points of modern app builders:
Google doesn't see your Lovable app the way you do.
In this post, we'll break down how Googlebot interprets client-side rendered (CSR) pages, why it often misses your content, and what you can do about it without leaving Lovable.
The Two-Phase Way Google Sees the Web
Before understanding what happens to your Lovable app, let's peek behind the curtain of Googlebot.
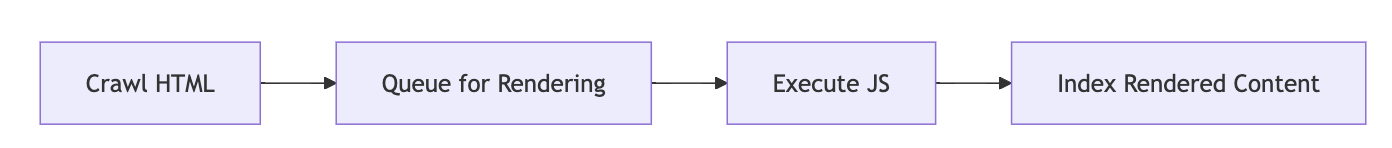
Google doesn't index a webpage in one go. It uses a two-step process:
- Crawl phase:
Google fetches your HTML and scans it for links and text. - Render phase:
Later, Google uses a headless Chrome instance to execute JavaScript and try to render the page like a browser.
Sounds simple, right? But here's the catch: rendering is expensive, delayed, and sometimes skipped entirely.
That means if your Lovable app serves minimal HTML at first, Google might never see your real content.
What Client-Side Rendering Looks Like on Lovable
Lovable apps are typically client-side rendered. The browser receives an almost empty HTML shell and loads everything else through JavaScript.
Here's what a basic Lovable app might send to Googlebot:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My Lovable App</title>
<meta property="og:title" content="My Lovable App" />
<meta property="og:description" content="Build amazing products with AI" />
<meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/og-image.png" />
<meta property="og:url" content="https://my-app.lovable.app" />
<meta property="og:type" content="website" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script src="/main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>All your app's components, text, meta tags, and Open Graph data are loaded later, inside /main.js.
When Googlebot first crawls this page or any other page on your site, it sees only that index.html shell and its empty <div id="root"></div>.
The content it needs to understand your app just isn't there yet.
The Problem with Other Crawlers
While Google can technically execute JavaScript, it doesn't always do so reliably. And here's the bigger issue: other crawlers often don't render JavaScript at all.
This includes:
- LLM crawlers (PerplexityBot, GPTBot, ClaudeBot)
- Bing's crawler
- SEO analysis tools
- Legacy search engines
These bots see exactly what's in your initial HTML. Nothing more.
Why Lovable Breaks SEO
When your content and metadata are injected after load, several SEO problems arise:
Missing content: Googlebot can't read your headings, text, or product details in the crawl phase.
Empty titles and meta tags: Many CSR frameworks insert titles and descriptions dynamically, which don't appear in raw HTML.
No structured data: Schema markup added via JavaScript won't be available during initial crawling.
Broken Open Graph tags: Social previews fail because og:title, og:description, and og:image are loaded after the fact.
Delayed rendering: Google may wait hours or even days to render your page, delaying indexing.
This is why no matter how many prompts you send to Lovable to fix your page titles and descriptions, it never gets reflected in the browser.
Your app is live, but to search engines, it looks like an empty shell.
How to Test What Google Actually Sees
You can easily test how Google views your Lovable app.
Option 1: Use curl
Run:
curl -L https://your-app.lovable.app
You'll see the raw HTML that Googlebot sees during its crawl phase.
If the output doesn't contain your page content, Google can't index it properly.
Option 2: Use Google Search Console
- Go to URL Inspection for your app
- Click "View Crawled Page"
- Compare the "Crawled HTML" vs "Rendered HTML"
Often, you'll notice the crawled HTML is empty or missing important tags.
Option 3: Use our Free Bot & Crawler Test Tool
Use HadoSEO's Free Bot & Crawler Test Tool to see your site exactly the way Google's crawler sees it and compare it to what should be seen.
Sample Output Comparison
Raw HTML (what crawlers see first):
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script src="/main.js"></script>
</body>Rendered HTML (what appears after JS executes):
<body>
<div id="root">
<header>
<h1>Welcome to My App</h1>
</header>
<main>
<p>Build amazing products with AI...</p>
</main>
</div>
</body>The difference is critical for SEO.
How to Fix Empty Page Content and Metatags (Without Leaving Lovable)
Now that you know what's happening, how do you fix it?
There are a few ways to make your Lovable app SEO-friendly:
1. Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
You could rebuild your app with SSR, but Lovable doesn't natively support server-side code execution meaning you'd lose access to making changes in Lovable. It's also overkill for many projects.
2. Static Site Generation (SSG)
SSG pre-renders your pages at build time, creating static HTML files for every route. However, you need to configure build-time rendering for every route and rebuild your entire site whenever content changes. For dynamic apps or those with frequently updated content, SSG quickly becomes impractical.
3. Prerender or Middleware Rendering
Some developers use middleware to render HTML snapshots for bots.
However, that means adding extra infrastructure: servers, proxies, and caching layers.
4. DNS Rendering (Easiest)
A new approach used by Hado SEO makes it effortless.
You keep building your app on Lovable, Replit, or Bolt.new.
When a bot visits your site, Hado SEO automatically renders your app on your behalf and serves complete HTML to the crawler.
No code changes. No hosting migrations. You simply point your DNS to our proxy server.
It's like giving Google the SSR version of your app, while users still get the fast CSR experience.
Visualizing the Difference
| Viewer | What They See | SEO Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Human user | Fully loaded Lovable app (JS rendered) | ✅ Perfect UX |
| Googlebot (without rendering) | Empty <div> | ❌ Not indexable |
| Googlebot (with Hado SEO DNS Rendering) | Full HTML snapshot | ✅ Indexable |
Key Takeaways
Google can technically render JS, but not always reliably.
Lovable apps are client-side rendered, so most of your SEO content isn't visible in the crawl phase.
To make your app indexable, you need a rendering layer that feeds search engines pre-rendered HTML.
The easiest solution? DNS rendering with Hado SEO. No backend required.
Pro Tip: Try This Yourself
Run this command to see what Googlebot sees:
curl -A "Googlebot" https://your-lovable-app.com
Then run the same command again with DNS rendering enabled and compare the results.
You'll see why Google suddenly understands your content.
Make Your Lovable App Visible to Google
Your app deserves to be found.
With Hado SEO, you can keep building where you love (on Lovable, Replit, or Bolt.new) and still enjoy server-side level SEO performance.
Related Reading: